About The Doctor
Specialising in Head & Neck Oncology Surgery, Reconstructive Surgery and Skull Base Surgery, Dr. Sarin brings along experience of more than 20 years in the field. Chandler Society & Mukut Sahariya awardee, Dr. Sarin has been instrumental in developing the Head & Neck Cancer Department and is trained as a clinical fellow in Head & Neck Ablative as well as Reconstructive surgery at the Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center, University of Miami, United States. His expertise lies in Oral Cancer, Throat Cancer, Thyroid surgery (including robotic surgery), Parathyroid surgery (including minimally invasive techniques), Parotid surgery, Tracheal reconstruction and Laser and Robotic resection for head & neck cancer. Dr Sarin is intimately involved in clinical and translational research and has passion for education.
Specialization
- Oral Cancer Surgery
- Thyroid and Parathyroid Surgery
- Complex Reconstruction of head and neck defects
- Robotic and Laser Surgery
Awards
- Chandler Society Award (USA), 2005
- Mukut Sahariya Award, 1997
- Kamani Charity Book Prize (Gold Medal in MS), 1997
Frequently Asked Questions About Oncology
How many kinds of tumours are there?
There are two kinds of tumour – Malignant & Benign. A benign tumour is more common, and is generally harmless. It doesn’t spread to other parts of body. A malignant tumour on the other hand, never stops growing unless until treated and can spread to other parts of the body. cancer is the name given to a malignant growth.
Is cancer contagious or infectious?
No. Since cancer is not caused by a germ, it is not “catching”, and cannot be transmitted from one person to another.
How does Cancer spread?
A malignant tumor is made up of cancer cells. When it first develops, this malignant tumor may be confined to its original site. This is known as a cancer in situ (or carcinoma in situ). If these cells are not treated, they may spread beyond their normal boundaries and into surrounding tissues, becoming invasive cancer. Some benign tumors are precancerous and may progress to cancer if left untreated. Other benign tumors do not develop into cancer. For a cancer to grow bigger than the head of a pin, it must grow its own blood vessels. This is called angiogenesis. Sometimes cells move away from the original (primary) cancer, either by the local tissue fluid channels (lymphatics) or in the blood stream, and invade other organs. When these cells reach a new site, they may continue to grow and form another tumor at that site. This is called a secondary cancer or metastasis.
What are the warning signs of Cancer?
The chances of curing cancer increase with early detection. The Indian Cancer Society and other organizations recommend paying attention to seven warning signs of cancer:
– Changes in bowel or bladder habits
– Unusual bleeding or discharge
– A sore that does not heal
– Indigestion of difficulty swallowing
– A nagging cough or hoarseness
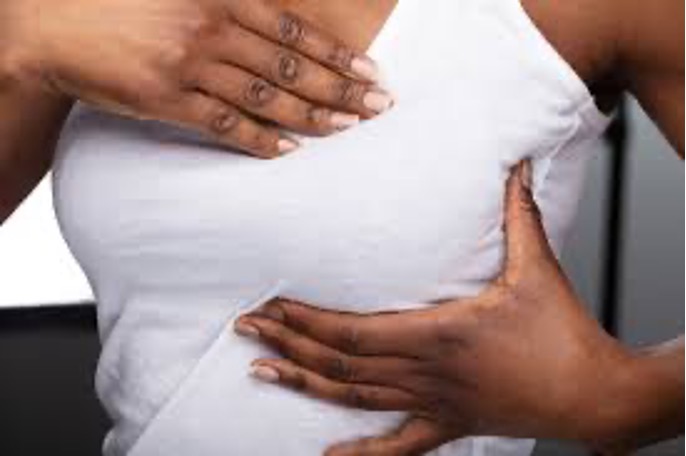
– A thickening or lump in the breast or elsewhere
– An obvious change in wart or mole
A physician can detect cancer by taking medical history, performing routine check ups, cancer screening tests, imaging techniques and tissue biopsy.
What is Chemotherapy used for?
Chemotherapy is given for the following reasons:
– Shrink tumors
– Slow cancer’s growth
– Keep the cancer from spreading
– Relieve diseases related symptoms
– Prolong survival
Chemotherapy is used to treat many different types of cancer. The type, location, and stage of the cancer as well as your general health will largely determine if chemotherapy is appropriate and which agents ought to be used.
What are the benefits of taking treatment through MMT instead of directly from the doctor?
We provide services from top doctors across top hospitals to ensure that you get the best treatment.