Cervical Cancer Surgery
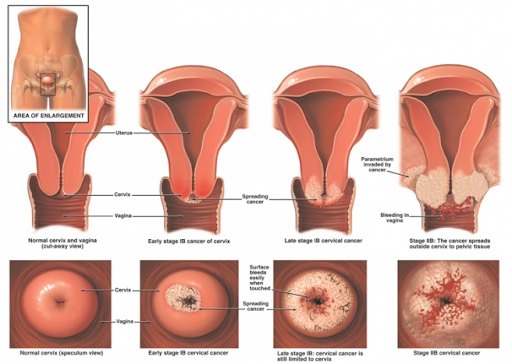
According to the World Health Organization, cervical cancer is the fourth most common cancer among women. It is cancer of the cervix which is located in the lower part of the uterus connected to the vagina.
Today, we at MyMedTrip.com, shall brief you on cervical cancer among women. We will give you information on what is cervical cancer, symptoms of cervical cancer, cervical cancer treatment, and cervical cancer surgery with cost. Alongside this, you will also get some important details such as the success rate of cervical cancer surgery in India.
| Particulars | Details |
|---|---|
| Cost of cervical cancer surgery in India | 5, 000 – 6,000USD |
| Discount | 10% on the above quoted price (final hospital’s bill) ONLY APPLICABLE ONLY FOR MyMedTrip.com patients Click here for exceptions and terms. |
| Number of days at hospital (Estimated) | 2 -3 days |
| Number of days in India outside hospital (Estimated) | 22-30 days |
| Treatment’s Success Rate | 66-92% |
| Tests required to help assess the treatment | Biopsy, HPV typing test, MRI, CT Scan, and PET CT scan cell test. |
What is covered in the above mentioned cost for surgery?
This price includes surgery cost, doctor’s fee, standard prescribed tests and all standard expenses required at the hospital.

About the cervix
The cervix is located in the lower part of the uterus and is therefore connected to the vagina. It is a cylindrically shaped network of tissues that connects the vagina with the uterus.
It consists of fibromuscular tissues and is divided into two parts, ectocervix and endocervix. The ectocervix is projected into the vagina and through this, it leads to the endocervix.
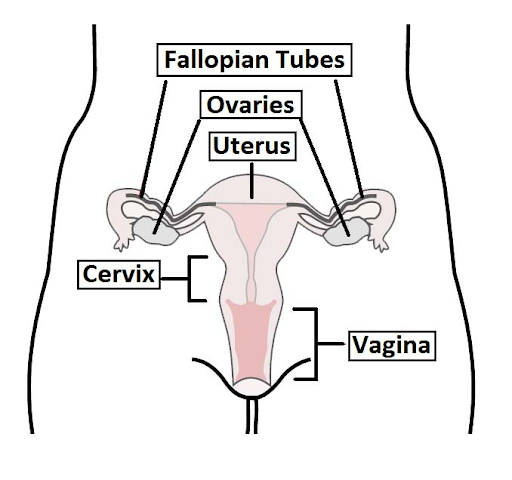
The main function of the cervix is to allow the passage of sperms, maintain sterility of the female reproductive tract, and prevent any infection via bacterial invasion.
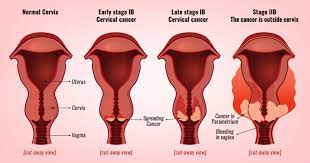
Cervical cancer
Cervical cancer is the uncontrolled growth of cells in the cervix region. It occurs among women over 30 years of age and is mostly caused by long-term infection of the human papillomavirus otherwise known as (HPV).
HPV is a common virus that is sexually transmitted. Although getting infected with the virus is very common among people who are sexually active, getting cervical cancer through this is rare. Only in the case of a long lasting HPV infection or persistent HPV infection, does one have the chance of developing cervical cancer.
Cervical cancer is mostly of two types, squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Squamous cell carcinoma is more common than adenocarcinoma and is caused when cells that cover the outer portion of the cervix grow out of control. Adenocarcinoma on the other hand is when cells from the cervical canal, known as glandular cells, grow out of control.
There are some other types of cervical cancer that are not very common. They are adenosquamous carcinoma, clear-cell carcinoma, and small-cell carcinoma. Adenosquamous carcinoma is the cancer comprising two kinds of uncontrolled cell growth, squamous cells and glandular cells.
Causes of cervical cancer
One of the major causes of cervical cancer is the HPV is a virus that is sexually transmitted. Upon exposure, the body’s immune system immediately begins to fight and prevent it from causing harm. However, the virus sometimes persists and has the capacity to survive for years.
Although there is no direct link between HPV and cervical cancer, research suggests that it contributes to it to a great extent. This occurs usually when the HPV causes mutations in the cervical cell’s DNA.
Our DNA is responsible for a cell’s growth and it’s death. When mutation occurs, there is malfunctioning that causes an exponential growth of cells and no cell death.
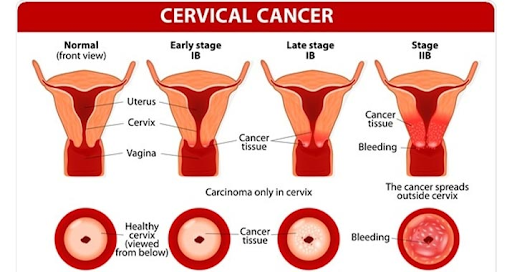
This growth leads to the formation of sheets of tissues that accumulate and become a tumour. A tumour could either be cancerous or non-cancerous. The word cancerous is used when cell-growth continues in other parts of the body even after the formation of tumour .
Cancerous cells found in other parts of the body that had originated in the cervix are termed as secondary cancer.
Risk factors for cervical cancer
Risk factors make a person more prone to the development of a specific disease. In the case of cervical cancer, the risk factors include:-
- Multiple sexual partners
- Sexually transmitted infections such as AIDS and herpes.
- Smoking.
- A compromised immune system.
- Exposure of a fetus to miscarriage prevention drugs.
- Age.
- Oral contraceptives.
Symptoms of cervical cancer
The symptoms of the various types of cervical cancer are:-
- Bloody vaginal discharge .
- Abnormal bleeding during menstruation.
- Vaginal bleeding after hitting menopause.
- Pelvic pain.
- Leg pain.
- Back pain.
- Extreme fatigue,
- Weight loss.
- One swollen leg.
- Vaginal bleeding after intercourse, during menstruation, or after menstruation.
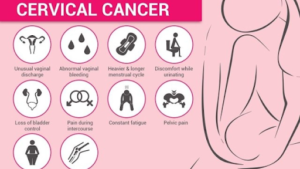
In its initial stages, cervical cancer does not cause any symptoms. It is only in the later stages that the cancer becomes symptomatic. This is evident through bleeding after intercourse or any other irregular bleeding from the vagina.
Despite this, it is difficult to diagnose cervical cancer. This is mainly because vaginal bleeding is also symptomatic of other diseases such as an infection. It is thus best to visit the doctor when any of the above mentioned symptoms begin to appear.
Tests for cervical cancer diagnosis
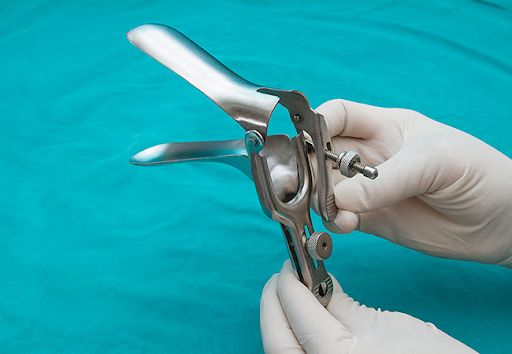
After a patient reports the aforementioned symptoms, the doctor recommends some tests. These tests vary based on the symptoms, the age, and overall health of the patient. Other factors such as the family history of the patient, the results of any earlier medical tests, and finally the type of cancer suspected also play a significant role.
Mentioned below are some tests suggested for a cervical cancer suspect.
- Bimanual pelvic examination and sterile speculum examination- In this test, the doctor manually checks the patient’s reproductive organs with the help of a speculum which keeps the vaginal walls open.
- Pap test- In this test the doctor scrapes some portions from the inside and outside of the cervix. This is then examined with the help of a computer to determine any unnatural cell growth.
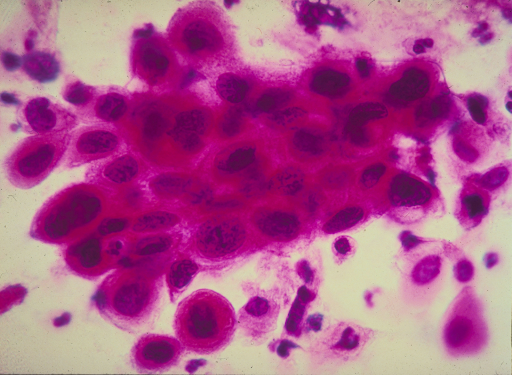
3. HPV typing test- This is done in a manner similar to pap test and is suggested when the pap test results show some signs of unnatural cell growth. In this, the doctor’s main aim is to find out if there is any presence of HPV virus.
4. Biopsy– It is the main test that confirms the presence of cancerous cells. In a biopsy, a portion of the cervix is extracted out and examined under a microscope.

If the biopsy test results confirm the presence of cancer then further tests are prescribed to determine its spread. This is done under a gynecologic oncologist who takes over after the biopsy tests results. The tests are:-
- Pelvic examination- This test is done under anesthesia to examine the extent of cancer spread in the nearby regions.
- CT scan- It reveals the body’s organs via x-rays from different angles.
- MRI- This discloses the size of the tumor in the patient’s body organs. In this magnetic resonance test, the patient is made to consume some amount of dye that enhances the body’s detailed images.
- PET-CT scan- It is usually recommended alongside a CT scan to examine the body’s different organs more closely. In this test, the patient is given a small amount of radioactive sugar that cancer cells absorb more aggressively.
- Molecular testing- This test is conducted in a laboratory to determine the specific characteristics of the tumor.
Treatment for cervical cancer
The test results determine which specific treatment is to be given to the patient. The standard method of treatment involves surgical intervention along with radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy.
Types of surgery for cervical cancer
Surgery is conducted when the cervical cancer is within the range of the cervix. There are various ways to surgically remove a cancerous tumor from the cervix region.
-
Conization
This is a method that is similar to the way a biopsy is conducted. However, instead of removing a small portion of tissue for examination, the surgeon removes the entire range of cancerous tissues. It is usually done to remove microinvasive or very small tumours.
-
Hysterectomy
This procedure completely removes the uterus including the cervix. It is also known as simple hysterectomy. Against this, there is radical hysterectomy. In a radical hysterectomy, the cervix, the uterus, the upper vagina, and tissues surrounding the cervix are removed entirely.
-
Bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy –
This procedure involves the removal of the fallopian tubes and both ovaries. It is done alongside a hysterectomy.
-
Radical- trachelectomy –
This involves the removal of only the cervix. It is done on younger patients who have plans of preserving their fertility.
-
Exenteration
This involves the removal of the uterus, vagina, lower colon, and other areas where the cervical cancer has spread. This is usually done after radiation therapy in cases where the cancer has persisted or staged a return.
Surgical intervention is recommended only in the case of early-stage cancer. In this stage, the cancer cells lie within the cervix. Therefore, surgically removing them is an effective way to treat cancer.
These surgical interventions may be conducted as open surgery, which is the more traditional method involving longer inclusions. Another way is the microsurgical method that involves smaller incisions and a faster recovery.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy is given to patients whose cancer has spread and/or remained despite the surgery.
Radiation therapy, also called external-beam radiation therapy, is either given through external beams. It is also given through internal beams, known as internal- beam radiation therapy. Usually a combination of both is given for more effective results and to prevent the cancer’s return.
Medications for cervical cancer
Medicines are given for stopping cancer cell growth (chemotherapy) and increasing immunity (immunotherapy). The medicines prescribed by the doctor differ from patient to patient.
Risks of cervical cancer treatment
The risks or side-effects of the treatment depends on the method used to treat cancer. If surgery is conducted then the common side-effects specific to surgeries, are:-
- Infection at the surgical site.
- Excessive bleeding.
- Blood clots.
Common side effects of other treatments include:-
- Anemia
- Appetite loss
- Constipation
- Dehydration
- Fatigue
- Hair loss
- Heart problems
- Joint pain
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Skin conditions
- Weight gain
- Weight loss
- Thyroid problems
- Nerve problems
- Sleeping problems
These aforementioned side-effects are the most commonly found side-effects. They do not occur all at once. In order to get a clearer picture of the probable side-effects, it is best to openly discuss the possibility of having side effects with the doctor.
How can MyMedTrip.com help?
If you have decided to travel to India for Cervical Cancer surgery, you may contact us on our Whatsapp number +91 9818237391 or email us at hi@mymedtrip.com The first consultation arranged by us is free of cost! We also provide visa invitation letters and help in facilitating the medical journey to India.
Throughout the journey, you shall be provided with one of our staff members for proper guidance through linguistic barriers, even though most of the hospitals and doctors we feature are well versed with Arabic, Russian, Bengali, and English.
If you have any further queries or questions related to Cervical Cancer surgery in India, please do not hesitate to email us at the aforementioned address.
Frequently Asked Questions about Cervical Cancer Surgery
What is cervical cancer?
Cervical cancer is cancer in the cervix region.
What causes cervical cancer?
The exact cause of cervical cancer is unknown but research has shown that it is linked to HPV virus infection.
What preventive measures to take if I am more prone to cervical cancer?
Maintaining a sexually healthy lifestyle will make you less prone to HPV virus and thus reduce chances for cervical cancer.
Who is more prone to cervical cancer?
People with multiple sexual partners and an unhealthy sexual habit are more prone to cervical cancer. Smoking is another cause that will enhance the risks of developing this disease.
Can cervical cancer be treated?
If it is diagnosed at an earlier stage, treatment is possible.
Will I need surgery?
Surgery is only recommended when the cancer is contained within the cervix.
What are the alternatives to surgery?
Discuss with your doctor on the availability of alternatives to surgery. You could also opt for the ‘clinical trial’ method which implies that any new methods of treatment will be performed on you for its treatment and research purposes.
Is there any way to prevent HPV virus infection?
Vaccines are available for HPV virus infection.
Is India a good option for cervical cancer treatment?
Most of the hospitals in India are nationally and internationally accredited. This means, Indian hospitals are at par with global standards of medical care. All of the hospitals featured by MyMedTrip.com have international and national accreditation.
Is it possible to conceive after cervical cancer diagnosis?
There is only one kind of surgery, which is radical-trachelectomy, that preserves fertility. However, it is best to discuss this issue with the doctor.
How to cope with cervical cancer?
There are support groups for patients dealing with cervical cancer and the families involved. You could also opt for one-on-one counseling sessions with a professional psychologist.