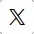Breast Cancer
Breast cancer develops when cells in the breast multiply and divide uncontrollably, resulting in a lump of tissue known as a tumor. It can strike both men and women, although it affects women significantly more. Breast cancer is the second most frequent cancer in women, after skin cancer.
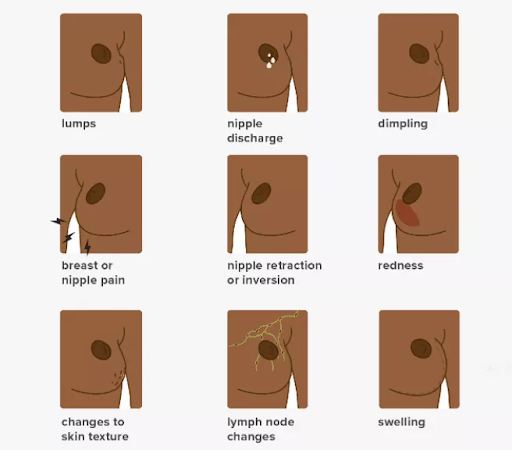
Breast cancer starts in the tissue of the breast. It develops when cells in the breast mutate or alter and multiply out of control, resulting in a mass of tissue. Breast cancer, like other cancers, has the ability to enter and expand into the tissue that surrounds the breast. It can also spread to other places of the body, resulting in the formation of additional tumors. This is known as metastasis.
Breast cancer symptoms include feeling a lump in the breast, observing abnormalities in the skin of the breasts, and experiencing a change in the size of the breast. Early detection can be aided by mammograms.
Symptoms of Breast Cancer
It is a known fact that when abnormal cells in the breast proliferate and multiply, breast cancer develops. However, experts are unsure of the actual breast cancer causes.
According to research, there are a number of risk factors that can raise the chances of having breast cancer. Here are some of them:
- If an individual is 55 or older, they are more likely to develop breast cancer.
- Breast cancer is far more common in women than in men.
- If there are breast cancer-affected parents, siblings, children, or other close relatives, then there is more likelihood to have the disease at some point in life. Approximately 5% to 10% of breast cancers are caused by single faulty genes that are passed down through generations.
| Particulars | Details |
|---|---|
| Cost for breast cancer treatment in India | 2000 to 7000 USD |
| Discount | 10% on the above quoted price (final hospital’s bill) ONLY APPLICABLE ONLY FOR MyMedTrip.com patients Click here for exceptions and terms. |
| Number of days at hospital (Estimated) | 2 to 7 days (length of the stay depends on the type of surgery) |
| Number of days in India outside hospital (Estimated) | 3 to 4 weeks |
| Treatment’s Success Rate | 99%(localized cancer) 86% (regional cancer) 28%(metastatic cancer) |
| Tests required to help assess the treatment | Blood Test, Mammogram, Positron emission tomography (PET) scanning, Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), ultrasonography, biopsy, Breast Assessment, Breast Augmentation. cell test. |
What is covered in the above mentioned cost for surgery?
This price includes surgery cost, doctor’s fee, standard prescribed tests and all standard expenses required at the hospital.
India, A Preferred Destination For Breast Cancer
India has some of the best breast cancer treatment hospitals. These hospitals provide novel medical and diagnostic services, including the use of cutting-edge technology. Patients flock to India for medical care because of the low cost of mammograms and breast cancer therapy offered by hospitals.
India, the United States, United Kingdom, Germany, and France are among the finest countries for breast cancer therapy. However, in industrialized countries, the cost of surgery and therapy is relatively costly.
However, in India, the cost of treatment is roughly half of that without sacrificing the outcome. The cost-effectiveness is due to superior comprehensive surgical care and technical advancements that meet worldwide standards.
The Indian healthcare system offers well-trained doctors and specialized surgical and post-operative care teams that can handle difficult cases at a fair cost. Medical, surgical, and radio oncologists, among others, work at hospitals with modern technology and an experienced team of oncologists.
Apart from the hospital, the success and survival rates of the oncology team at the hospital should also be considered when looking for a doctor for breast cancer treatment.
Some of the reasons why international patients prefer India for breast cancer treatment are the facilities provided by the hospitals that meet both national and international accreditation criteria.
Along with this, the staff at India’s best breast cancer treatment hospitals are all fluent in English. The doctors have a good understanding of the patients’ requirements. For their patients, India’s top doctors employ third-generation technology as well as medical approaches.
The top hospitals in India have a diverse range of surgical oncologists on staff, as well as a medical team. The surgeons have the knowledge and ability to handle the most basic to the most complex cases.
Indian Medical Visa Process (India e-Medical Visa)
By default, the Indian government allows a medical visa to be valid for 60 days. However, India’s new visa policy allows the paper-based medical visa to be extended for up to 180 days.
Individuals can obtain an Indian Medical Visa by filling out an Indian Visa Application Form online. This procedure will only take a couple of minutes. Then you have to make the payment through PayPal and provide the appropriate documents for treatment, such as a letter from a hospital. This process takes 72 hours to complete, and an accepted Visa is emailed to the concerned person.
Nationals of e-Visa India-eligible countries who require a Medical Visa may apply online using the online e-Visa India application form at https://www.indiavisa-online.org. A letter from the hospital in India where they intend to receive treatment is required.
The individual may also be requested to show proof that they have enough money to cover their medical expenses in India. They may also be asked to produce a return travel ticket to their native country once the medical treatment is completed. These papers can be faxed or emailed to the Help Desk, or they can be submitted to the website later.
One of the benefits of the Indian Medical Visa is that, unlike the 30-day Tourist Visa, which is only valid for two entries, it enables three entries into India during its 60-day duration.
The following conditions and requirements of the e-Visa for medical treatment must be understood and remembered as pointers:
- The Indian e-Medical Visa is valid for 60 days from the date of arrival in India.
- The e-Medical India Visa allows you to visit India three times.
- Individuals can apply for a Medical Visa up to three times per year.
- It is not possible to extend the electronic Medical Visa.
- This visa is not convertible and cannot be changed to a tourist or business visa.
- It can’t be used to enter protected or restricted sites.
- Patients must show proof of financial support for their stay in India.
- During your trip to the airport, the patient must have a PDF or paper copy with you.
- On the e-Medical India Visa, patients can request a return ticket.
- There is no such thing as a group medical visa for India; each applicant must apply independently.
- On the day of arrival in India, the passport must be valid for at least six months.
- Individuals must have two blank pages in their passports so that immigration and border control personnel can stamp their passports at the airport for entry and exit.
- A regular passport is required to be presented. Indian Medical Visas cannot be obtained using diplomatic, service, official or refugee passports.
- Individuals must apply for a paper or conventional India Medical Visa rather than an electronic Medical Visa on the Govt. website if the treatment will continue longer than 180 days.
The website allows a person to apply online, and it will take you 3 to 5 minutes to finish the application. It is highly recommended that an individual applies for a Medical Visa in India online rather than visiting an Indian Embassy or High Commission.
Breast Cancer Procedure
Breast cancer comes in a variety of types. Ductal carcinoma, which starts in a milk duct, is the most frequent type of cancer. Another form is lobular carcinoma, which starts in a lobule, one of the small milk glands.
Breast cancer that is “invasive” means that cancerous cells have spread to adjacent tissue. The cancer is then more prone to spread to other places of the body.
Breast cancer that is “noninvasive” remains in its original location. These cells have the potential to become invasive in the future.
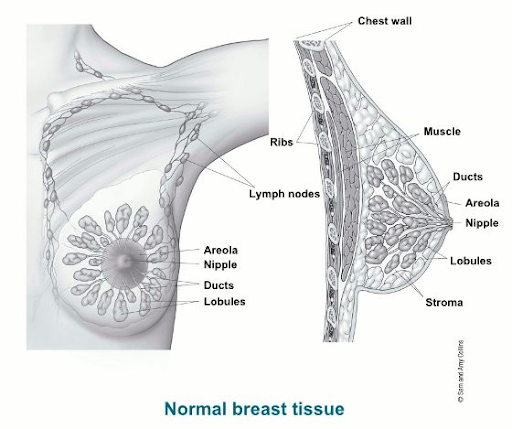
The size of the tumor and whether it has spread to lymph nodes or other places of the body are used by doctors to assess the cancer stage.
Breast cancer stages vary in a variety of ways. The stages 0–4 are included in one, with subcategories at each stage. Each of these major stages is described below. Substages can reveal details about a tumor’s features, such as its HER2 receptor status.
- Stage 0: This stage is also known as in situ ductal carcinoma. The malignant cells have only spread to the ducts and not to the surrounding tissues.
- Stage 1: The tumor is up to 2 centimeters (cm) wide at this stage. No lymph nodes have been damaged, or there are small groupings of cancer cells in lymph nodes.
- Stage 2: The tumor has grown to a size of 2–5 cm in diameter but has not migrated to the lymph nodes. Or it has grown to 2 cm in diameter and has initiated its spread to neighboring lymph nodes.
- Stage 3: The tumor has expanded to numerous lymph nodes and is up to 5 cm in diameter, or it is bigger than 5 cm and has spread to some lymph nodes.
- Stage 4: The cancer has spread to other parts of the body, most commonly the bones, lungs, liver, or brain.
Breast cancer is frequently diagnosed as a consequence of routine screening or when a person reports symptoms to a doctor. The tests and procedures that the doctor carries out helps in making and confirming the diagnosis. The panel of doctors generally follow a sequence to the treatment.
-
Early Disease
Surgery, followed by chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy, is the treatment sequence for someone with an early disease. Hormone therapy may be required in some circumstances.
-
Locally Advanced disease
Doctors usually recommend NeoAdjuvant chemotherapy followed by surgery in such circumstances. In some circumstances, radiation therapy as well as hormone therapy may be required.
-
Metastatic Disease
- Single Metastasis/ oligomers: Treatment is similar to that of a locally progressed illness, with the addition of further radiation to the metastatic location.
- Multiple metastases: In addition to hormone therapy and radiation therapy, palliative chemotherapy is used.
Breast Cancer Treatment Options
The surgeon determines the treatment plan after determining the breast cancer stages and progression of the disease. The majority of the time, it’s a multi-modality approach.
The most common therapy for breast cancer is surgery. Surgery, on the other hand, must be combined with additional treatments like chemotherapy, targeted therapy, radiation, or hormone therapy.
Breast Cancer Surgery
Surgical intervention may be required for a variety of reasons:
- The goal of surgery is to remove as many cancer cells as possible. Whether it is a breast-conserving surgery or a mastectomy.
- Sentinel lymph node biopsy or axillary lymph node dissection can be used to see if cancer has spread to neighboring lymph nodes under the arm.
- Breast reconstruction surgery restores the form and appearance of the breast following cancer removal.
- To alleviate the signs and symptoms of advanced breast cancer
Types of Breast Surgery
-
Lumpectomy or removing the breast cancer
The surgeon eliminates the tumor plus a short margin of good tissue surrounding it during a lumpectomy. This is also known as breast-conserving surgery or wide local excision.
For smaller tumors, a lumpectomy may be considered. Chemotherapy may be used before surgery to reduce a tumor and allow it to be removed completely using a lumpectomy technique in some persons with larger tumors.
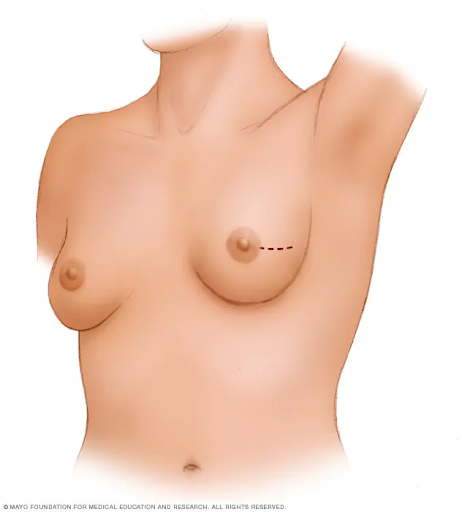
2. Mastectomy or removing the entire breast
A mastectomy is a procedure in which all of the breast tissue is removed. The lobules, some skin, including the nipple and areola, ducts, fatty tissue, are all removed during most mastectomy surgeries.
In some circumstances, newer surgical methods to improve the appearance of the breast may be an option. Breast cancer operations such as skin-sparing mastectomy and nipple-sparing mastectomy are becoming more popular.

3. Sentinel node biopsy or removing a limited number of lymph nodes
The surgeon might discuss the role of removing the lymph nodes that receive the lymph drainage from the tumor. This will help him to assess the progression of the lymph nodes.
If no cancer is detected in those lymph nodes, there is a slim likelihood that cancer will be found in any of the other lymph nodes, and no additional lymph nodes will need to be removed.
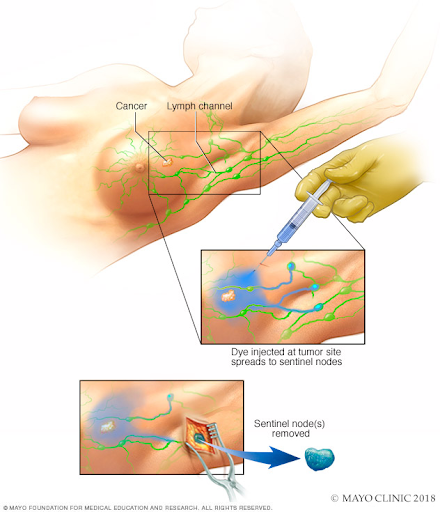
4. Axillary lymph node dissection
Several lymph nodes under the arm are removed during this operation. In an axillary lymph node dissection, the number of nodes removed varies depending on the patient. For all women with early-stage breast cancer who have tiny quantities of cancer in their sentinel lymph nodes, it may not be necessary.
In women who are having a lumpectomy and radiation therapy, and who have a smaller tumor and no more than two sentinel lymph nodes, a full axillary lymph node dissection is usually avoided. Its goal is to lower the procedure’s risk of negative effects while maintaining survival.
5. Removing both breasts
There can be a possibility of having a high risk of cancer in the other breast due to a genetic predisposition or a strong family history. Then the patient might choose to have their second healthy breast removed. This is known as contralateral preventive mastectomy.
Breast cancer surgery complications are determined by the procedures you select. Pain, bleeding, infection, and arm swelling are all possible side effects after breast cancer surgery (lymphedema). Following surgery, the patient may elect to have their breasts reconstructed. The patient will be advised to refer to a plastic surgeon before the breast cancer surgery.
-
Breast reconstruction
This is a procedure for reconstructing the breast following a mastectomy or lumpectomy. Breast reconstruction can be done at the same time as cancer removal surgery, which is referred to as immediate reconstruction. It can also be done months to years later, which is referred to as delayed reconstruction.
There are several reconstruction alternatives available, including a prosthesis or a tissue flap technique. Breast reconstruction is an option for many women who have had a mastectomy for breast cancer. The goal is to restore the breast’s natural look following surgery.
For some patients who are having breast-conserving surgery, the doctor may recommend grafting fat into the damaged breast to conceal any dimples that may remain after the procedure. There are various forms of reconstructive surgery, and a woman may select one based on her specific needs.
-
Breast Implant
These are prosthetic implants that are implanted beneath the skin to give the breasts a more natural appearance. Saline-filled implants and silicone gel-filled implants are the two most frequent types of implants. The saline-filled implants feature a silicone outer shell that is filled with sterile saline or salt water on the inside.
Instead of seawater, a silicone gel-filled implant is filled with silicone gel. There are a variety of other implant types available, each with its own shape and texture. Each implant has its own set of advantages and disadvantages. The implant that is chosen differs from one person to another.
-
Tissue flap procedure
The surgeon uses muscle and tissue from other parts of the body to restructure the breast in this manner. A pedicle flap is a type of tissue flap surgery that uses tissue from the back or belly. Without cutting any blood vessels, this flap is transported to the chest. The surgeon cuts the blood vessels and the relocated tissue is linked to the new blood vessels in the chest in a free flap operation.
The doctor may also advice certain prophylactic measures to lower the risk of cancer
Prophylactic mastectomy: This is a prophylactic operation that involves removing the breast to reduce the chance of breast cancer in those who are at high risk.
Ovarian removal as a preventative measure: This is a preventative technique for lowering estrogen levels in the body. Its goal is to reduce the likelihood of estrogen stimulating or assisting in the occurrence of breast cancer.
Radiation Therapy
To kill cancer cells, radiation therapy uses high-powered beams of energy such as X-rays and protons. Radiation therapy is usually performed with the use of a huge machine that shoots energy beams on the body, external beam radiation. However, the patient can also expose themselves to radiation by putting radioactive material orally, brachytherapy.
Following a lumpectomy, external beam radiation of the whole breast is often performed. If the patient is at a low risk of cancer recurrence following a lumpectomy, then breast brachytherapy may be carried out.
For larger breast tumors or malignancies that have progressed to the lymph nodes, doctors may consider radiation therapy to the chest wall after a mastectomy.
Depending on the treatment, breast cancer radiation might last anywhere from three to six weeks. A radiation oncologist chooses which treatment is appropriate for the patient based on the cancer kind, tumor location and general wellbeing.
Radiation therapy has side effects such as fatigue and a red, sunburn-like rash. Breast tissue may also look enlarged or firmer. More significant issues, such as damage to the heart or lungs, or, in rare cases, second malignancies in the treated area, may arise.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a type of treatment that uses medications to kill fast-growing cells, such as cancer cells. If the cancer has a high risk of recurrence or spreading to other parts of the body, then the doctor advises chemotherapy after surgery to reduce the risk of recurrence.
Chemotherapy is sometimes administered to women with large breast tumors before surgery. The goal is to reduce a tumor to the point where it can be surgically removed.
Chemotherapy is also utilized in the treatment of women whose cancer has progressed to other sections of their bodies. It may be prescribed to help manage the cancer and alleviate any symptoms it causes.
The adverse effects of chemotherapy are determined by the medications you are given. Hair loss, nausea, vomiting, exhaustion, and an increased risk of infection are all common adverse effects.
Hormone Therapy
Hormone therapy is used to treat hormone-sensitive breast cancers. Progesterone receptor-positive (PR-positive) and Estrogen receptor-positive (ER-positive) malignancies are the terms used by doctors to describe these tumors.
Hormone therapy can be given before or after surgery or other treatments to reduce the risk of cancer recurrence. It may reduce and control cancer that has already spread.
The goal of the treatment is to block hormones from acting on cancer cells, preventing them from proliferating further. Hot flashes, nocturnal sweats, and vaginal dryness are all possible adverse effects of hormone therapy, depending on the exact treatment.
Targeted Drug Therapy
This is the most advanced form of breast cancer treatment. It is costly, but the results are promising. Targeted medication therapy differs from chemotherapy in that it targets specific properties of cancer cells. Targeted medication therapy, unlike chemotherapy, does not harm healthy cells.
Tips and Advice
Once the patient is discharged from the hospital there will be an external drainage device in place post-surgery. The drains will collect and eliminate fluid from the surgical area.
Before the patient leaves the hospital, the doctor will show how to care for the device. This usually entails clearing the drains, monitoring the fluid, and keeping an eye on any potential issues.
The amount of fluid draining will decrease over time. The color of the fluid can also shift from cherry-red to yellow-red, then to straw. The drainage system is usually removed 1 to 3 weeks after surgery.
After surgery, the patient will be given a special bra to keep the bandages in place. The doctor will advise when to remove this bra and show how to change the surgical dressings.
One of the most important thing to do is for the first week after surgery, keep the incision clean and dry. It is possible that they take sponge baths rather than showers. Bathing in a bathtub is acceptable as long as the incision area is kept dry.
Over the incision, small fragments of tape will remain. They typically fall off on their own. Following breast cancer surgery, the region may appear black and blue. In a few days, this will be gone. They may have tingling or numbness in the inside region of the upper arm or in the armpit. This is normal.
The doctor will prescribe medication for pain relief. Daily stretching exercises can help restore mobility, but the patient should consult the surgeon about when to begin. Before resuming driving, consult the doctor. After 10 to 14 days, most women are able to resume driving.
It is critical to have regular follow-up appointments. The doctor will keep a careful eye on the patient to make sure cancer hasn’t returned. Exams of the chest, underarms, and neck are common during checkups.
The patient may be advised to have a mammogram in 6 to 12 months, then once a year after that, depending on the type of surgery they had. Women who have had a mastectomy (complete breast removal) may no longer require a mammogram on that side.
A woman who has had cancer in one breast is more likely than the norm to acquire cancer in the other. They should continue to self-examine the breasts on a monthly basis, checking both the treated and unaffected breasts. Any changes should be immediately reported to the doctor.
How Can MyMedTrip.com Help You?
It is natural to be overwhelmed and concerned while traveling to a new place for medical treatment. Throughout the journey, we shall assist the patient and their attendant, and provide a manager for help throughout the whole medical trip. We will also assist in overcoming linguistic barriers.
Should you decide on traveling to India for medical assistance, you may email us at hi@mymedtrip.com or WhatsApp at +91 9818237391. The first consultation arranged by us would be free of cost! Additionally, we also provide visa invitation letters and help in facilitating the medical journey to India.
For any further assistance/queries or questions related to breast cancer as well as services in India, do not hesitate to email us at the aforementioned address. We shall be glad to assist you and help you get well soon.
Frequently Asked Questions about Breast Cancer
How long does it take to recover from breast cancer?
Chemotherapy treatments for early-stage breast cancer usually last three to six months, although the doctor may change this depending on unique circumstances. Advanced breast cancer treatment can last up to six months.
Is it possible to entirely cure breast cancer?
There is no “natural” cure for breast cancer. Medical interventions are necessary to eradicate, decrease, or slow the growth of tumors. Alternative therapies and lifestyle changes can, however, be used in conjunction with standard medical treatments to help reduce breast cancer symptoms.
How long do people have to go through chemo for breast cancer?
Chemotherapy cycles normally last two to three weeks. The schedule varies depending on the medications taken. Some treatments, such as chemotherapy, are only given on the first day of the cycle. Others may receive it once a week or once every other week for a few weeks.
When is surgery performed after a breast cancer diagnosis?
The time between diagnosis and procedure is usually less than 90 days. Lumpectomy, mastectomy, and lymph node removal are the three surgical techniques most typically used to treat breast cancer.
Is it okay if I wish to follow a particular diet after my breast cancer treatment?
As a breast cancer operation is a major surgical procedure, food restrictions are in place. The exact diet, on the other hand, may only be given by the dietician at the time of the release.
What can be done to prevent breast cancer?
Restricting alcohol use, maintaining physical activity levels and weight, avoiding tobacco and radiation exposure, and limiting hormone therapy are all ways to prevent breast cancer. Breastfeeding is recommended for new moms to reduce the risk of breast cancer.
What is the nature of breast cancer pain?
A malignant lump can appear anywhere in the breast and feel spherical, mushy, and painful. The lump might be painful in some circumstances. Breast tissue that is thick and fibrous is also found in some women. If this is the case, it may be more difficult to detect lumps or changes in the breasts.
At what age can a woman be diagnosed with breast cancer?
The majority of breast cancers are diagnosed in women over the age of 50. Some women will develop breast cancer despite having no other known risk factors.
How can I find out whether I have breast cancer at home?
Try looking at the breasts directly in front of the mirror. Changes in skin texture, such as dimpling, puckering, indentations, or skin that resembles an orange peel, should be looked for. Take notice of each breast’s form and outline. Examine whether the nipple is turning inward..
Where are breast cancer lumps found?
Breast cancer lumps are more commonly discovered in the upper outer quadrant of the breast in women. They’re frequently located near the nipple of guys. Breast cancer can start anywhere there is breast tissue, from the breastbone to the armpit to the collarbone, regardless of gender.
How long does the treatment plan last for breast cancer?
The treatment plan lasts for up to five years.