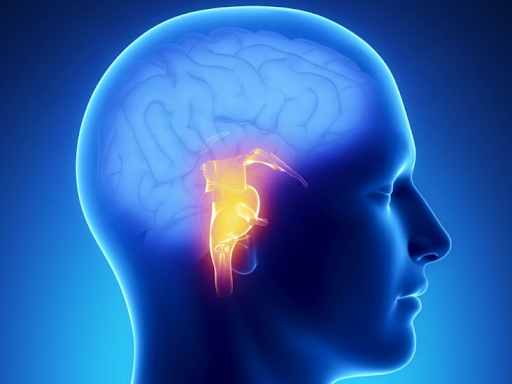
Brain tumour treatment
A brain tumour is the abnormal growth of cells inside the skull. This group of mass may be malignant and non-malignant. When a tumour is cancerous, it grows and causes pressure on other parts of the brain with the capacity to severely damage parts of the brain.
Today, we at MyMedTrip.com shall brief you on what brain tumours are and the various kinds of brain tumour treatment. We will also share with you detailed information on brain tumour treatment procedure and brain tumour treatment success rate in India, alongside sharing with you the details of brain tumour operation cost in India.
| Particulars | Details |
|---|---|
| Brain tumour surgery cost in India | US$ 5,000 to 10,000 (depending on the medical case of the patient) |
| Discount | 10% on the above quoted price (final hospital’s bill) ONLY APPLICABLE ONLY FOR MyMedTrip.com patients Click here for exceptions and terms. |
| Number of days at hospital (Estimated) | 5 days |
| Number of days in India outside hospital (Estimated) | 14 days |
| Treatment’s Success Rate | 90% (22-44 yrs) |
| Tests required to help assess the treatment | MRI, CT scan, PET scan, Biopsy, ECG etc. |
What is covered in the above mentioned cost for brain tumor surgery?
This price includes surgery cost, doctor’s fee, standard prescribed tests and all standard expenses required at the hospital.
Brain tumour
A brain tumour is a serious life-changing disease. The exact cause of this is unknown.
However, a brain tumour is divided into two categories, primary and secondary. Primary brain tumours are abnormal cell-growth originating within the brain. Secondary brain tumours on the other hand are abnormal cell-growth that have originated elsewhere and have begun spreading to the brain.
Although secondary tumours spread faster than primary tumours, the spread of both kinds of tumours within the skull can severely damage parts of the brain.
Before getting into a discussion on this therefore, let us look at the anatomy of the brain and its functions.
About the brain
In the anatomical structure of the brain, there are three different parts. They are the brainstem, the cerebellum, and the cerebrum. The cerebrum is the largest part and is sub categorised into the right and left hemispheres.
The cerebellum is situated after the cerebrum at the back of our head. The brainstem is located at the end of the brain and connects the entire brain to the spinal cord.
Together these three components along with the spine comprise the Central Nervous System which is responsible for major functions of our body.
Functions of the brain
The brain which is part of the CNS is responsible for our everyday functions such as talking, walking, breathing etc. These functions are controlled by the three sub-sects. The cerebrum is responsible for voluntary activities such as seeing, speaking, talking, feeling etc.
The cerebellum is responsible for activities that maintain balance such as walking and running. The brainstem is responsible for involuntary activities such as breathing.
When tumours grow inside the skull of the person, it severely damages parts of the brains with complicated impacts on our everyday living.
The various kinds of brain tumour
Brain tumours, apart from their primary categorization into primary and secondary tumours, are further subcategorized under these primary and secondary types. Before starting off with the subategorizations, it is to be noted that primary brain tumours usually do not grow much and are thus known as low grade tumours.
However, in some cases that they do begin to grow, they will be referred to as high grade tumours.
Secondary tumours are also known as metastatic cancer because they result from cancer that originated in other parts of the body such as the lungs or blood, and has spread to the brain.
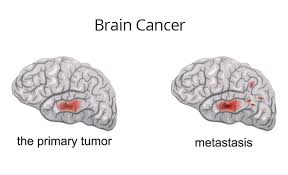
The various subtypes of brain tumours are:-
1. Glioma
This is the most common subtype of primary brain tumours. They occur in the glial cells which are present throughout the CNS. They are also present in the peripheral nervous system. There are different types of glial cells in the brain that serve different supportive functions. Glial cells are referred to as the ‘glue’ of the nervous system because they are the main pillars of support to the nervous system.
2. Astrocytoma
Astrocytoma that takes its name after the glial cell astrocyte, a star shaped glial cell, is the most common type of glioma tumour. These cells are mostly found in the cerebellum and cerebrum. Cancers of these cells occur mostly among children.
These tumours are further categorized into grade I, grade II, grade III, and grade IV. While grade I astrocytoma are mostly non-malignant, the rest are malignant. Grade II astrocytoma grows slowly, grade III grows fast, and grade IV is the most aggressive of all.
3. Oligodendroglioma
Oligodendrogioma takes its name after the glial cell oligodendrocyte, responsible for the production of myelin. Myelin is a fatty substance that protects the nerves. Oligodendroglioma, that originates in the brain, can either be low grade which means that they won’t grow much. When they do begin to grow, they are known as anaplastic oligodendroma.
4. Ependymoma
Ependymoma takes its name after the glial cell epididymal. Epididymal cells are responsible for the brain’s homeostasis. Ependymoma originates in the brain but can also grow in the spine. These may also occur among children.
5. Meningioma
This type is mostly non-malignant and originates in the meninges, the protective covering that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. Meningioma, even though are mostly non-malignant, will cause serious symptoms if they begin to grow at an unprecedented rate and cause pressure on the brain.
Some other kinds of brain tumours are craniopharyngioma, which begins in the pituitary gland of the brain or schwannoma which is very rare.
Symptoms of brain tumour
As there are many types of brain tumours that affect different areas of the body, it is difficult to categorise the overall symptoms of brain tumour. Some general symptoms of brain tumours however will be:-
- Persistent headache.
- Seizures.
- Control-loss in the body’s Function. Control-loss in
- Consciousness.
- Breathing difficulty.
- Confusion.
- Weakness.
- Numbness.
Along with these symptoms, some other pertinent symptoms include memory problems, sleeping problems, the body’s balancing problems etc.
Diagnosis of brain tumour
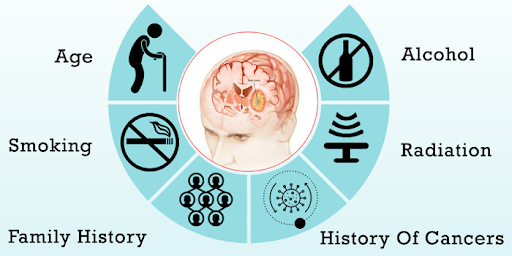
Diagnosis of a brain tumour depends on various kinds of tests. Some of them are:-
- MRI
- Biopsy
- CT scan
- PET scan
- Angiogram
- ECG
There are some other tests as well such as vision tests in which an eye examination would reveal the impact of the tumour on the person’s ability to see. After the results have been given, and a tumour is revealed, the doctor suggests some more tests to determine the degree of its progression and to learn more about it.
Treatment of brain tumour
1. The multidisciplinary team
In order to give the most effective treatment to a patient, a treatment plant is created by a team of medical professionals that come from various arenas. Some of these officials will be:-
- Oncologists
- Oncologist nurses
- Psychologists
- Social workers
- Radiologists
- Dietitians
- physicians
2. Making the treatment plan
After a team has been formed, the team will proceed to cart a treatment plan. This is largely dependent on facts such as the location of the tumour, the progressions of the tumour, the impact of the tumour on the patient’s everyday life, the degree of the tumour’s spread to other parts of the body etc. The medical team also takes into account the side effects of the treatment and the patient’s overall physical health alongside his/her preferences.
3. Surgery
For non-malignant tumours, surgery covers the removal of the tumour. However, there always remains a chance of its recurrence. For malignant tumours, a surgery alongside radiation therapy and chemotherapy is recommended as part of the treatment plan.
The surgery to be conducted for removal of the tumour is known as craniotomy. A craniotomy involves surgically removing one part of the skull due to swelling of a part of the brain. This part is later replaced by a bone graft after completion of the surgery.
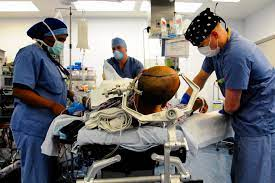
There are various sub-types of craniotomy such as an endoscopic craniotomy or a biopsy. In an endoscopic craniotomy, a special instrument called the endoscope, which is attached to a camera and lens, is used.
The endoscope gives the internal images of the brain and guides the surgeon through the surgery so that it may be performed with utmost precision. In a biopsy, only a section of the brain is removed to evaluate it for malignant or non-malignant tumours.
4. Radiation therapy
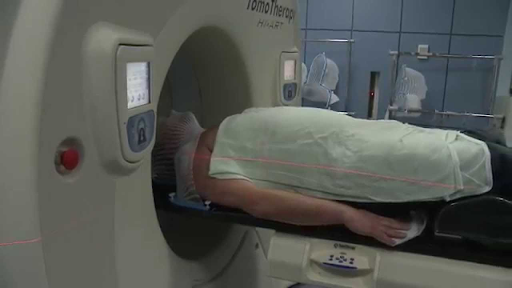
Radiation therapy is given by a radiation oncologist and is conducted through progressive sessions, usually after surgery. There are two kinds of this therapy called external beam therapy and internal beam therapy. In an external beam therapy, the radiation is given from the outside via a machine. In an internal beam therapy, implants inside the body are used to give radiation and damage the cancer growing cells.
5. Chemotherapy
Alongside radiation therapy, medications are also used to destroy the cancer cells further. Chemotherapy medications may be used either orally or through the IV line and either will be given at the location of tumour or directly into the bloodstream.
The main function of chemotherapy medicines is to damage the cancer cells, control its further growth, and make the cancer symptoms almost negligible.
Side-effects of brain tumour treatment
Because of the wide array of tumours of the brain, it is very important that a patient discusses the side-effects of the treatment plan prior to its beginning. This not only prepares the patient for combating them, but also helps them decide whether to proceed with the treatment or not.
However there are some general side-effects, some of which are:-
- Anemia
- Appetite loss
- Psychological problems
- Constipation
- Cough
- Dehydration
- Fatigue
- Headaches
- Hair loss
- Infection
Undergoing cancer treatment is most pertinent to combating cancer. However, the very procedure can be quite taxing on the individual and their family members. Therefore, visiting counselling sessions may help the family and the individual to physiologically combat the disease.
How can MyMedTrip.com help you?
Once you have decided to travel to India for this treatment, you may contact us on our Whatsapp number +91 9818237391 or email us at hi@mymedtrip.com. The first consultation arranged by us is free of cost!
We also provide visa invitation letters and help in facilitating the medical journey to India. Throughout the journey, you shall be provided with one of our staff members for proper guidance through linguistic barriers.
Although, most of the hospitals and doctors we feature are well versed with Arabic, Russian, and English. If you have any further queries or questions related to brain tumour treatment in India, please do not hesitate to email us at the aforementioned address.
Frequently Asked Questions about Brain tumour treatment
What is a brain tumour?
A brain tumour is the abnormal growth of cells inside the skull.
What are the functions of the brain?
Some functions of the brain include functions in our everyday life such as talking, walking, breathing etc.
What are the different kinds of brain tumours?
Broadly there are two categories of brain tumour, primary and secondary.
What are some types of primary brain tumour?
Some types of primary brain tumours are glioma, astrocytoma, oligodendroglioma, ependymoma, meningioma etc.
What is malignant brain tumour?
Malignant tumours are tumours that are cancerous and are more likely to spread to other parts of the body.
What is non-malignant brain tumour?
Non-malignant brain tumours are tumours that are noncancerous. They have lesser chances of spreading from its place of origin.
Who devises the treatment plan for brain tumour treatment?
A multidisciplinary team devices the treatment plant for brain tumour.
What is a treatment plan for treating brain tumour?
The treatment plan includes surgical intervention, radiation therapy, chemotherapy etc.
What is the surgical procedure for brain tumour called?
The surgical procedure for removing a brain tumour is called craniotomy. A craniotomy involves surgically removing one part of the skull due to swelling of a part of the brain. This part is later replaced by a bone graft after completion of the surgery.
What is chemotherapy?
Alongside radiation therapy, medications are also used to destroy the cancer cells further. This is called chemotherapy.
What are some of the side-effects of brain tumour treatment?
Some side-effects of tumour treatment include anemia, appetite loss, psychological problems, constipation, cough, dehydration, fatigue, headaches, hair loss etc.
How many days do I have to stay in the hospital for spine fusion surgery?
Usually, patients are required to stay for two days from the surgery day.